tgoop.com/neurocognitionandlearning/4507
Last Update:
Sleep Resets Neurons to Keep Learning Possible
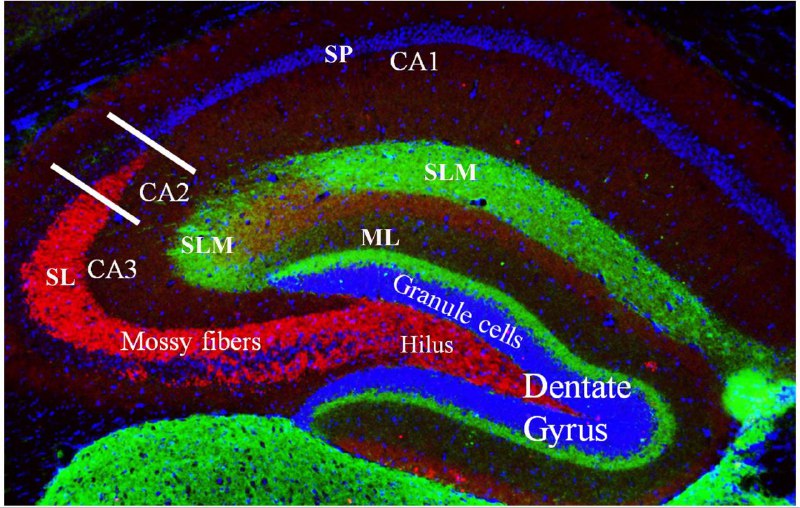
During sleep, the brain resets memory by silencing specific neurons in the hippocampus, allowing for continuous learning without overloading. This process, crucial for memory consolidation, involves different regions of the hippocampus, particularly CA2, which helps reset memory circuits.
Researchers believe this mechanism could be used to enhance memory or potentially erase traumatic memories. The study provides insight into why sleep is vital for maintaining cognitive function and memory.
The hippocampus is divided into three regions: CA1, CA2 and CA3. CA1 and CA3 are involved in encoding memories related to time and space and are well-studied. During sleep, the neurons in the CA1 and CA3 areas reproduce the same neuronal patterns that developed during learning in the day.The CA1 and CA3 regions that had been very active were suddenly quiet. It’s a reset of memory, and this state is generated by the middle region, CA2.
🧠🆔 @neurocognitionandlearning
BY Neuroscience & Psychology
Share with your friend now:
tgoop.com/neurocognitionandlearning/4507
